Pumped Storage Plants Pdf
European statistics (EUROSTAT) showed that, until some years ago, Romania has been considered a country without pumped storage plants (PSPs). Currently, Romania appears to have a total capacity of 91.5 MW, installed in five pumped storage plants operated by Hidroelectrica within their hydropower developments portfolio. The paper presents the hydropower developments of PSPs type in Romania; and an evaluation of their electricity production with emphasis on the renewable component, as well. Previous article in issue. Next article in issue.
More than 200 pumped storage units installed worldwide by VoithIn 1937, Voith developed the first large, single-stage pump turbine, which operated both as a turbine for energy generation and in the reverse direction as a pump. Today, nearly 200 Voith pump turbines have been installed worldwide with a combined output of more than 25 000 megawatts. With a wide range of specific speeds, pump turbines can be installed at sites with heads up to 800 meters and with unit capacities ranging from less than 10 to 500 megawatts. Voith is continually advancing its state-of-the-art technological capabilities with developments that include variable-speed technology and wide head range applications. These machines have proven extremely reliable in practical operation.
Hybrid solutions – such pumped storage power plants combined with wind and/or solar farms – are becoming increasingly important for the generation and storage of clean, renewable energy, as well as in the production of drinking water.With the innovative concept of combining wind power and hydropower together, the upper basin is integrated into the foundation of the wind turbine towers. Planning and infrastructure costs, as well as environmental impact, can be reduced as the two technologies use the same grid connection and switchgear.Combining the technologies creates new trading alternatives that are not possible in a pure wind farm operation. This is expanding the potential of decentralized pumped storage.Should the wind turbines deliver more energy than needed, water is pumped from the lower basin into the upper basin of the wind turbines. If there is no wind blowing or a higher demand of energy arises, the water flows from the upper basin through the turbine into the lower basin. This will drive a turbine that will generate via the connected motor generator electricity and release it into the grid. The use of saltwater for pumped storage plants with the ocean as the lower reservoir, instead of using precious fresh water, offers a huge potential. This symbiotic saltwater concept could be an application for small grids on islands.
Joseph Nye is university distinguished service professor and former dean of Harvard's Kennedy School of Government. He has served as assistant secretary of defense for international security affairs, chair of the National Intelligence Council, and deputy under secretary of state for security assistance, science, and technology. His recent books include Soft Power: The Means to Success in World Politics, Understanding International Conflicts (7 th edition), The Power Game: A Washington Novel, and The Powers to Lead. Joseph nye understanding international conflicts.
Pumped Storage Environmental Impact

The challenges of protecting equipment against corrosion can be solved technically.By combining a seawater pumped storage system and a desalination plant, using reverse osmosis (RO) to turn seawater into drinking water, we can help provide fresh water in arid coastal areas and environmentally friendly energy at the same time. The ocean would be used as the lower reservoir, with the upper reservoir in nearby coastal mountains. The principle behind the operation of pumped storage power plants is both simple and ingenious. Their special feature: They are an energy store and a hydroelectric power plant in one. If there is a surplus of power in the grid, the pumped storage power station switches to pumping mode – an electric motor drives the pump turbines, which pumps water from a lower reservoir to a higher storage basin. If the demand for electricity in the grid rises, water is released from the upper basin via a pressure pipeline to the bottom.
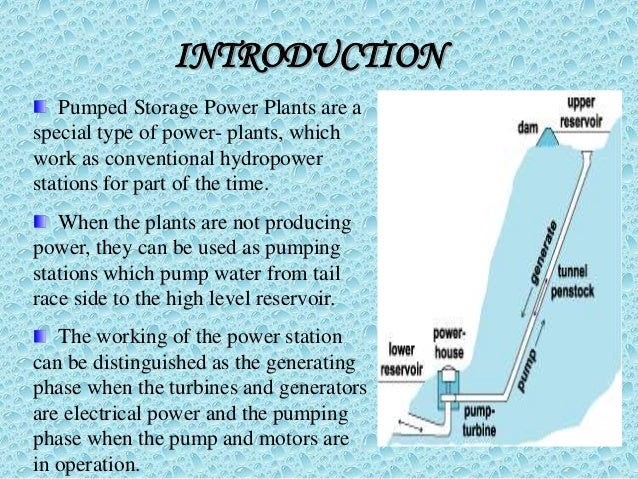
The water causes the pump turbines to rotate, now operating in turbine mode and used to drive the generators. Within seconds, electricity is generated and fed into the grid. In order to achieve the required drop height for his turbine experiments, Voith constructed an uphill water storage tank in neighboring Schlossberg. From there, the water rushed through pipes into the Brunnenmuehle. If the tank was empty, water was pumped up from the bottom again. Through this research institute at the water mill, Voith almost inadvertently constructed Germany's first pumped storage plant.

It was commissioned on 14 November 1908. The Brunnenmuehle is still used as Voith Hydro's research and development center. It was fully modernized in 2008.
Comments are closed.